To answer the question of 'how much does it cost to produce one ton of alternative fuel', it is necessary to analyze and think from multiple perspectives. The following is a step-by-step analysis process:1. Definition and classification of alternative fuelsAlternative fuels refer to the use of combustible waste to replace traditional natural fossil fuels for production. The application of combustible waste in industry can not only save energy, but also contribute to environmental protection. Common alternative fuels include garbage derived fuel (RDF), solid recycled fuel (SRF), tire derived fuel (TDF), biomass fuel, and municipal sludge.2. Economic analysis of alternative fuelsThe economy of alternative fuels depends not only on production costs, but also on their calorific value and comparison with fossil fuels. According to relevant information, the calorific value of alternative fuels is usually lower than that of coal, but by increasing the calorific value and reducing the heat loss coefficient ratio,


Recycling old mattresses to produce refuse-derived fuel (RDF) is an effective way to reduce waste while generating an alternative energy source. This process converts mattress components such as foam, textiles, and wood into usable fuel, supporting the circular economy and reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels.The Significance of Mattress Waste RecyclingMillions of mattresses are discarded each year, and their bulky nature makes them challenging to manage in landfills. Mattresses contain materials like polyurethane foam, steel springs, wood, and fabric, many of which are non-biodegradable. Recycling these components not only prevents landfill overflow but also enables the recovery of valuable materials for other uses, such as RDF production.The RDF Production Process from Recycled MattressesCollection and SortingDiscarded mattresses are collected from households, businesses, and institutions. They are sorted to remove non-recyclable items and contaminants, ensuring a clean feedstock for the recycling


In the economically dynamic Yangtze River Delta region of China, a waste textile alternative fuel production line with an annual capacity of 100,000 tons is set to be commissioned. This innovative production line will provide efficient and environmentally friendly RDF (Refuse-Derived Fuel) to a cement kiln operated by a state-owned enterprise, replacing traditional coal and significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The project not only accelerates the green transformation of the cement industry but also stands as a key development in the circular economy sector.The Yangtze River Delta is a global hub for textile and garment production, generating vast quantities of clothing each year, which inevitably results in substantial textile waste. Effectively managing this waste has long been a challenge. This 100,000-ton per year alternative fuel production line converts waste textiles into high-energy RDF fuel, addressing the local processing capacity shortage while reducing fossil fuel usage. The project


In the pulp and paper production process, will produce a variety of solid waste (i.e., slag), for example, an annual production capacity of 1 million tons of paper mills, the amount of slag accounted for about 10% of the amount of slag, i.e., 100,000 tons / year, which is a large number, and highly concentrated, such as improper disposal, but also cause significant pollution and endanger the ecological environment. The composition of paper production waste is very complex, mainly contains: rope, cotton yarn, cotton cloth, paper residue, wood chips, rubber, plastic, electronic parts, wire, nails, aluminum cans, PE plastic bottles, waxed paper and glass, stone and sand. Paper waste residue can be used to make solid alternative fuels, a utilization that not only reduces waste, but also replaces traditional fossil energy sources and reduces carbon emissions. The plastics in paper production waste can not be degraded, and direct stacking seriously affects the ecological environment. At present, there are paper


Industrial waste is composed of waste generated during the industrial production process, which can be in the form of solid, liquid, or gas. The industrial waste we usually refer to mainly refers to industrial solid waste. These industrial wastes need to be properly treated to reduce their impact on the environment and human health. Common treatment methods include recycling and reuse, incineration for energy conversion, landfill, etc.Converting industrial solid waste to Renewable Fuel, RDF is a feasible waste disposal method. RDF is a combustible fraction extracted from waste, typically used for energy production such as power generation or heating.The following are the general steps for converting industrial waste into RDF:1. Collection and Classification:Firstly, industrial waste needs to be collected and classified. The purpose of classification is to separate combustible and non combustible parts for subsequent processing.2. Shredding or Crushing:The collected industrial waste will be sent to a shredder

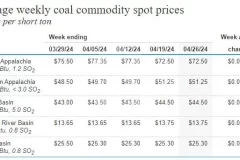
What is the price of RDF/SRF?
2024-05-06The pricing of RDF (Refuse-Derived Fuel) and SRF (Solid Recovered Fuel) per ton is a significant concern for investors and users alike. It goes beyond just investment returns, impacting the operational costs of users directly. Much like coal pricing, RDF/SRF pricing varies based on factors such as its source, quality, and market dynamics.RDF-5 PelletsThe U.S. Energy Information Administration website outlines prices for different coal grades and sulfur content, highlighting the disparities in coal pricing. When considering RDF/SRF for fuel application, factors like calorific value, post-combustion emissions, and potential impacts on the environment or end products are crucial. For example, RDF with high chlorine content may affect concrete quality when used in cement kilns.Average weekly coal commodity spot pricesHowever, determining RDF/SRF pricing is more complex than coal pricing. Firstly, there's no specialized RDF/SRF category in the spot or futures market. Secondly, RDF/SRF comes from various sources
At present, organic industrial waste generated by industries such as garment, shoe-making, tanning, textile, clothing, leather goods, packaging and plastic products mainly contains high concentrations of organic matter and some heavy metals. The common treatment method is direct incineration, but due to insufficient combustion, it is easy to cause serious secondary pollution and difficult to meet environmental standards. Processing these wastes into homogeneous and easy-to-burn refuse-derived fuels is another treatment method. However, such organic industrial wastes have problems such as poor adhesion and molding difficulties, and the organic matter in them may contain acid and sulfur, which may cause pollution in subsequent processing and fail to meet environmental protection requirements. To improve on these shortcomings of existing technologies, AI Shred has introduced a new process for the preparation of refuse-derived fuels. This process has excellent adhesive properties and easy molding characteristics

RDF alternative fuel is a new type of fuel with many advantages, compared with traditional fuel, it has obvious advantages in environmental protection, resource utilization and economic benefits. One of the main advantages of RDF alternative fuel is that it is more environmentally friendly. It is usually made from waste or renewable resources, such as garbage, biomass, etc. It reduces dependence on fossil fuels, lowers greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants, and has positive significance for improving air quality. RDF has a higher calorific value, which provides more energy and improves the efficiency of energy utilization. This not only reduces fuel consumption, but also lowers energy costs.The preparation process of RDF is relatively simple. Generally speaking, it needs to go through the steps of waste collection, classification, crushing, drying, etc., and then it is processed into pellets or lumps of fuel with certain specifications. This preparation process not only can effectively utilize waste

There are several materials in municipal solid waste more suitable for preparing RDF (refuse derived fuel) to replace fuel. The following are some common examples:1. Plastic: Plastic is a common material in domestic waste, especially plastics such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP) and polystyrene (PS). These plastics have high thermal values and are suitable for preparation of RDF.2. Paper and cardboard: Paper and cardboard are renewable resources. They contain high cellulose, easy to burn, and relatively high thermal values.3. Textiles: Textiles, such as clothes, towels, and bedding, are usually composed of fibers and have a certain heat value.4. Wood and wood products: wood and products such as wood chips and wooden blocks are a natural fuel source with high heat value.5. Rubber and leather: Although the thermal value of rubber and leather is relatively low, they can be mixed with other high thermal components to improve the overall heat value of RDF.6. Organic waste: organic matter in kitchen waste


In a world where sustainability and resource conservation are of paramount importance, finding innovative ways to manage waste is crucial. Landfills, historically viewed as the final destination for waste materials, are now being reimagined as potential sources of valuable resources. One such resource is Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF), and GEP ECOTECH is at the forefront of transforming landfill waste into a sustainable energy source.The Challenge of Landfill WasteLandfills have long been associated with environmental concerns, from methane emissions to soil and water contamination. As waste piles up in these sites, there is an urgent need to not only minimize the environmental impact but also harness the untapped potential within these waste heaps. This is where RDF comes into play.What is RDF?Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF) is a sustainable energy source produced from the combustion of non-recyclable waste materials. These materials, typically found in landfills, include plastics, paper, cardboard, textiles, and more


Cement Plant Refuse Derived Fuel System
2024-01-03The cement industry is undergoing a positive and remarkable transformation: replacing fossil fuels with refuse derived fuels (RDF), solid recover fuels (SRF) or biomass. This measure helps to reduce carbon emissions, achieve more environmentally friendly cement production processes, and fulfill the commitment of cement enterprises to sustainable development.GEP ECOTECH is committed to promoting sustainable development in the cement industry, and we offer a variety of innovative alternative fuel solutions for this purpose. Our solutions cover various kinds of materials and feeding requirements, tailoring the best solutions for customers to ensure stable and high-quality fuel supply.Shredding SystemA powerful shredding system is the key to the successful production of high-quality RDF/SRF. GEP ECOTECH's multi-stage shredding system doesn't fear the challenges of complex materials. From pre shredder to shearing shredder, and the eye-catching single shaft shredder, our shredders' durability and trouble free


RDF Pellet Machine
2023-09-03RDF pellet machines are designed for the drying and forming of combustible solid waste. Their primary function is to transform waste into standardized block-shaped fuel, increasing the calorific value per unit volume and facilitating storage and transportation. In the field of waste management, these pellet machines play a crucial role by converting otherwise useless waste into economically valuable alternative fuel.On the production site, RDF pellet machines face a significant challenge related to humidity. While they offer a drying function, these machines are not specifically designed for drying. Excessive moisture content can result in high energy consumption and issues such as reduced output and poor forming effects.GEP ECOTECH has rich experience in waste-to-fuel conversion, offering a series of equipment from shredders, magnetic separators, air separators to forming machines. Our equipment has extensive material adaptability, capable of transforming various combustible wastes such as municipal solid


Paper Mill Waste Utilization Direction: Convert to RDF using the AIShred Industrial Waste System
2023-02-26According to statistics, the paper waste residue produced by a recycled paper production plant with an annual output of 1.5 million tons is about 180,000 tons/year or more. When paper mills use recycled materials to make paper, the production process produces a large amount of waste materials, including stranded rope and light slag. For these paper waste residues, they can be reused in applications such as incineration for power generation, metal recycling, plastic regeneration, etc. after treatment through a reasonable process. Can paper mill waste be made into RDF fuel rods?Paper mill waste can be made into RDF fuel rods. Most of the solid wastes produced by paper mills are combustible materials, and only a small amount of materials with recycling value. After processing, paper mill waste can be made into RDF fuel rods, which can be used in large circulating fluidized bed boilers to mix and couple power generation and replace the use of coal-fired fuel in a large amount, saving a large amount of coal-fired


AIShred RDF&SRF Alternative Fuel Technology
2022-07-12Internationally, Refuse Derived Fuel (hereinafter referred to as "RDF") is regarded as a new way of waste harmless, recycling and reduction. It has been widely used in cement, power generation and other industries. It is green, environmentally friendly, high quality and low price Alternative fuels (SRF/RDF) are the new trend of the future. The preparation of waste-derived fuel RDF is not limited by site and scale. It is suitable for small and medium-sized waste treatment plants to be scattered and manufactured, and then collected for power generation, which is conducive to improving the scale and efficiency of waste-to-energy power generation. Converting waste to waste-derived fuel (RDF) serves two purposes: it can reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, thereby solving problems in the waste field, and it can supply large coal-fired power plants, waste incineration plants, cement plants Provides a large number of alternative fuel RDF. AIShred RDF&SRF Alternative Fuel Achievement PathAIShred has


Fuel Processing for RDF, TDF and SRF
2022-05-05Since the beginning of the 21st century, more and more waste has been generated. In order to cope with the threat to the environment caused by the increase in waste, people have begun to use waste as fuel that can be burned in boilers for power generation or heating. We divide the fuel from waste into RDF, TDF, SRF according to different components and processing method of the waste. RDF(Refuse-derived fuel) is a fuel produced by sorting and shredding combustible materials contained in municipal solid waste (MSW) and industrial waste. Compared to fossil fuels, RDF is more affordable, abundant, and environmentally friendly. SRF(Solid Recovered Fuel) is a fuel produced by drying, filtering, and shredding solid waste, It is usually produced to meet the standards in Europe. The EN 15359 document gives the specifications for classifying SRF. Unlike RDF, SRF is a more refined material that is slightly more efficient than RDF, though it takes a more advanced process to make the fuel. TDF(Tire-derived fuel) is a